Mastering the Simple Present Tense; An In-Depth Explanation
محتوى المقال
I. Introduction
A. Importance of the simple present tense in English
The simple present tense is one of the most fundamental and widely used verb tenses in the English language. It plays a crucial role in conveying basic information, expressing habits and routines, and communicating general truths. Mastering the simple present tense can significantly improve your fluency in English, as well as your ability to understand spoken and written text.
B. Purpose of the blog post
This blog post aims to provide an in-depth explanation of the simple present tense and its various uses in English. By the end of this post, you will have a comprehensive understanding of the tense, as well as the tools and techniques needed to use it effectively. Whether you’re an English learner or simply looking to brush up on your grammar skills, this guide will serve as a valuable resource for mastering the simple present tense.
II. Understanding the Simple Present Tense
A. Definition and basic concepts
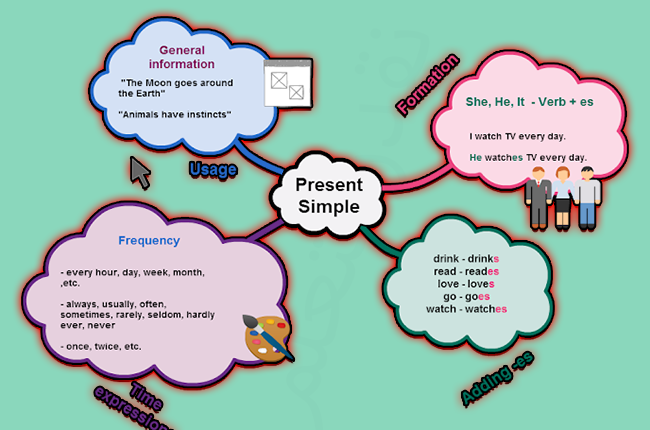
The simple present tense is a verb tense used to express actions or states that occur in the present time. It is formed by using the base form of the verb (e.g., ‘work’, ‘play’, ‘eat’) and adding an ‘s’ or ‘es’ to the end of the verb for third-person singular subjects (e.g., ‘he’, ‘she’, ‘it’). The simple present tense can be used in various contexts, as we will explore in the following section.
B. Common uses of the simple present tense
1. Facts and general statements
The simple present tense is used to express facts, general truths, or statements that are considered universally true. These statements do not change over time and are not specific to a particular moment.
Example:
Water boils at 100 degrees Celsius.
The Earth revolves around the Sun.
2. Habits and routines
We use the simple present tense to describe actions or events that occur regularly or repeatedly. This can include daily routines, hobbies, and habits.
Example:
.I eat breakfast every morning
She goes for a walk in the park on weekends.
3. Permanence and timeless statements
The simple present tense can be used to express situations or states that are considered permanent or long-lasting. It can also be used to describe timeless statements, such as proverbs or maxims.
Example:
Elephants have excellent memory.
Honesty is the best policy.
4. Scheduled future events
While the simple present tense primarily deals with the present, it can also be used to describe future events that are scheduled or fixed on a timetable. This is particularly common when talking about public transportation, meetings, and events.
Example:
The train arrives at 5 p.m.
The conference starts on Monday.
III. Forming the Simple Present Tense
A. Affirmative sentences
1. Subject-verb agreement
When forming affirmative sentences in the simple present tense, it’s crucial to ensure proper subject-verb agreement. This means that the verb should agree with its subject in terms of number (singular or plural). In general, for third-person singular subjects (he, she, it), an ‘s’ or ‘es’ is added to the base form of the verb, while other subjects use the base form without any changes.
Examples:
I work at a bank.
She works at a bank.
2. Regular verbs
Regular verbs follow the standard rules for subject-verb agreement in the simple present tense. The base form of the verb is used for all subjects except third-person singular, which requires the addition of ‘s’ or ‘es’ to the verb.
Examples:
We play soccer every weekend.
He plays soccer every weekend.
3. Irregular verbs
Irregular verbs do not follow the standard pattern of adding ‘s’ or ‘es’ in the simple present tense. The primary irregular verb in the simple present tense is ‘be’, which has three forms: ‘am’, ‘is’, and ‘are’. These forms are used according to the subject of the sentence.
Examples:
I am a teacher.
She is a teacher.
They are teachers.
B. Negative sentences
1. Using ‘do not’ and ‘does not’
To form negative sentences in the simple present tense, we use ‘do not’ (for plural subjects and ‘I’ and ‘you’) or ‘does not’ (for third-person singular subjects) before the base form of the verb.
Examples:
I do not like spinach.
She does not like spinach.
2. Contracted forms: ‘don’t’ and ‘doesn’t’
In informal speech and writing, ‘do not’ and ‘does not’ are often contracted to ‘don’t’ and ‘doesn’t’, respectively.
Examples:
We don’t go to the gym on Sundays.
He doesn’t go to the gym on Sundays.
C. Questions and short answers
1. Yes/no questions
To form yes/no questions in the simple present tense, use ‘do’ or ‘does’ at the beginning of the sentence, followed by the subject and the base form of the verb.
Examples:
Do you have a pen?
Does she have a pen?
2. Wh-questions
For wh-questions (who, what, when, where, why, and how), place the wh-word at the beginning of the question, followed by ‘do’ or ‘does’, the subject, and the base form of the verb.
Examples:
What do you do for a living?
Where does she live?
3. Short answers with ‘do’ and ‘does’
In response to yes/no questions, use ‘do’ or ‘does’ to form short answers, along with ‘not’ for negative responses. Remember to use the contracted forms ‘don’t’ and ‘doesn’t’ in informal contexts.
Examples:
Do you like pizza? Yes, I do. / No, I don’t.
Does he like pizza? Yes, he does. / No, he doesn’t.
Read more in Arabic about the simple present tense for easy understanding
IV. Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
A. Incorrect subject-verb agreement
One of the most common mistakes made by English learners while using the simple present tense is incorrect subject-verb agreement. This usually occurs when the verb form does not match the subject in terms of number (singular or plural).
To avoid this mistake, remember to add ‘s’ or ‘es’ to the base form of the verb for third-person singular subjects (he, she, it) and use the base form without any changes for other subjects.
Examples:
Incorrect: She work at a bank.
Correct: She works at a bank.
B. Confusion with the present continuous tense
Another common mistake is confusing the simple present tense with the present continuous tense. The simple present tense is used for facts, general truths, habits, and routines, while the present continuous tense is used for actions happening at the moment of speaking or around the present time.
To avoid this confusion, use the simple present tense for regular or unchanging situations, and use the present continuous tense (formed with ‘be’ + verb + ‘-ing’) for actions in progress.
Examples:
Incorrect: I am reading a book every day.
Correct: I read a book every day.
Incorrect: He reads a book right now.
Correct: He is reading a book right now.
C. Misuse of the simple present tense for past or future actions
Some English learners may mistakenly use the simple present tense to describe actions that took place in the past or will occur in the future. However, the simple present tense should only be used for actions or states that occur in the present, with some exceptions for scheduled future events.
To avoid this mistake, use the appropriate verb tense for past actions (e.g., simple past, past continuous) or future actions (e.g., simple future, future continuous).
Examples:
Incorrect: I go to the store yesterday.
Correct: I went to the store yesterday.
Incorrect: He arrives tomorrow.
Correct (if scheduled): He arrives tomorrow.
Correct (if not scheduled): He will arrive tomorrow.
V. Tips for Mastering the Simple Present Tense
A. Practice with everyday conversations and writing
One of the most effective ways to master the simple present tense is to incorporate it into your daily conversations and writing. Try to use the tense when describing your daily routine, habits, and general facts about yourself or the world around you. By using the simple present tense frequently, you will become more comfortable with its rules and nuances.
Examples:
I brush my teeth twice a day.
The sun rises in the east.
B. Use visual aids and charts to understand verb conjugations
Visual aids and charts can be helpful tools for understanding the different forms of verbs in the simple present tense. Create a chart or find one online that lists regular and irregular verbs, along with their conjugations for various subjects. By regularly referring to these charts, you can reinforce your understanding of the simple present tense and improve your overall grammar skills.
Example of a verb conjugation chart:
Subject
Regular verb (work)
Irregular verb (be)
I
work
am
You
work
are
He/She/It
works
is
We
work
are
They
work
are
C. Engage in language games and quizzes to reinforce learning
Language games and quizzes can be a fun and interactive way to practice and reinforce your understanding of the simple present tense. Many online resources and mobile apps offer grammar games and quizzes that specifically target the simple present tense. By engaging in these activities, you can test your knowledge, identify areas for improvement, and make learning more enjoyable.
Examples of language games and quizzes:
Online grammar quizzes focusing on the simple present tense
Mobile apps with games and exercises targeted at English verb tenses
Flashcards with simple present tense verb conjugations
VI. Conclusion
A. Recap of the importance and usage of the simple present tense
In this blog post, we have explored the various aspects of the simple present tense, including its definition, common uses, and formation. The simple present tense is a fundamental aspect of the English language, as it allows us to express facts, general truths, habits, routines, and, in some cases, scheduled future events. By understanding and correctly applying the rules of this tense, you can effectively communicate in both spoken and written English.
B. Encouragement for continued practice and mastery
Mastering the simple present tense is a crucial step in becoming proficient in English. While it may seem challenging at first, with consistent practice and dedication, you will find that your understanding and usage of this tense will improve over time.Use the tips and strategies provided in this blog post to help you in your journey toward mastering the simple present tense. Remember, practice makes perfect, so keep engaging in conversations, writing exercises, and language games to solidify your skills, and soon you’ll be confidently using the simple present tense in your everyday communication.